Let’s start with the bascis.
What is Video transcoding?
Video transcoding is the method of changing a video file from one format to a different. It entails altering a video file’s encoding format, decision, bit fee, or different parameters to make sure compatibility with totally different units, platforms, or web connection speeds.
Transcoding is essential in video manufacturing and distribution on any scale in anyway, and on this weblog submit, we’ll delve deep into video transcoding, offering you with complete information about its advantages, limitations, and best practices.
We’ll cowl the transcoding course of, types of transcoding, use instances, and the instruments and applied sciences accessible. By the top, you will clearly perceive the significance of transcoding for video manufacturing and streaming and be outfitted to make knowledgeable choices about optimizing your video content material for various units and platforms.
Let’s get began!
The Importance Of Video Transcoding In Today’s Digital Landscape
In a world the place digital content material is consumed on an ever-expanding array of units and platforms, video transcoding has develop into a necessary software to make sure seamless playback of video content material. Here are a number of the key explanation why video transcoding is so necessary:
- Compatibility: Different units and platforms have assist for various resolutions, bitrates, codecs, and container codecs. Transcoding allows seamless conversion into desired codecs which might be suitable with a wider vary of units and platforms.
- Optimization: Transcoding permits movies to be optimized for various units (desktops, smartphones, tablets, or good TVs) which all have totally different definitions for ‘optimum’ settings. By transcoding movies into resolutions and bitrates that make sure the smoothest playback for every on the best attainable picture high quality, you guarantee a greater viewing expertise for customers.
- Streaming: Transcoding is enterprise vital for OTT video streaming companies like YouTube, Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and so forth. These companies need to assist a variety of units, working methods, browsers… and even totally different brackets of web bandwidths! They use transcoding as an answer – optimizing their movies into a number of codecs and resolutions to make sure clean playback on a variety of consumer platforms and bandwidths.
- File measurement discount: Transcoding movies can even scale back the file measurement of the video, making it simpler and faster to add, share, or stream. This is very necessary when coping with massive movies.
- Accessibility: Closed captions and subtitles could be added throughout the transcoding course of, enabling customers with listening to impairments to grasp the content material of the video. Videos will also be transcoded with audio streams in numerous languages, to cater to non-native audio system.
Video transcoding is important in right this moment’s digital panorama for compatibility, optimization, accessibility, and environment friendly streaming of video content material throughout units and platforms.
Overview the video transcoding course of
“Transcoding” is an umbrella time period – the precise processes concerned differ from case to case. However, let’s take a look at an accepted normal for this course of.
The Input Stage
The first stage in video transcoding sometimes entails analyzing the unique video file to extract info such because the video and audio codecs, decision, bitrate, and body fee. This info is in comparison with these of the playback platform for use, to find out the optimum settings for the transcoded output file, and decide if a conversion is important.
If it’s, we transfer on to the transcoding pipeline.
The Transcoding Pipeline
A transcoding pipeline is a collection of steps concerned in transcoding a video file from one format to a different or optimizing it for various units and platforms.
Here are the steps concerned:
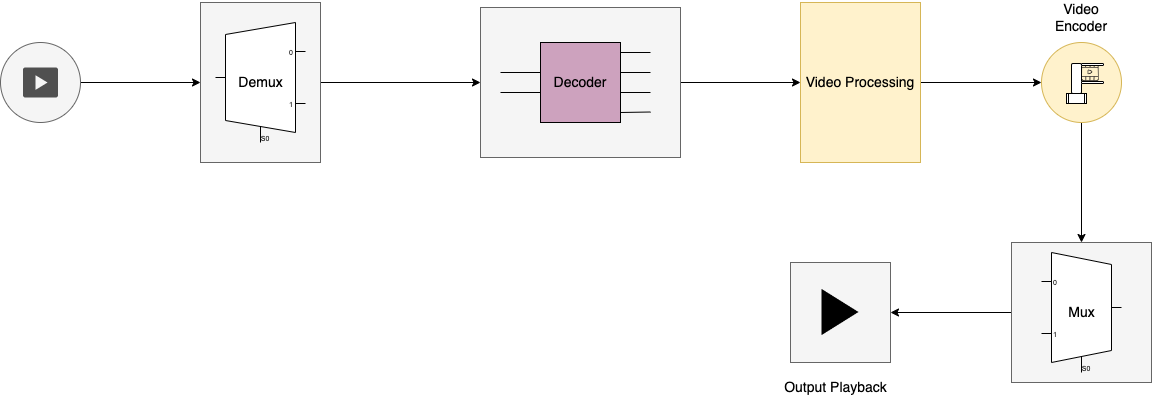
Step 1: Demuxing the enter
Demuxing (De-Multiplexing) is the method of analyzing a supply video file to establish its streams (video, audio, and subtitles) inside it and separating them into separate parts. Each element could be individually processed and optimized for the specified output format.
This separation is essential, as totally different streams require totally different processing and optimization methods to realize the specified output high quality. For instance, the video stream might must be resized or re-encoded at a unique bitrate, whereas the audio stream might require a unique sampling fee or compression format.
💡
For our instance, we’re solely masking optimization of the remoted video stream.
Step 2: Decoding the video stream
Once remoted, the compressed video stream is first transformed (decoded) into an uncompressed intermediate format, comparable to YUV or RGB, to make sure that the supply high quality is preserved.
Then, the video decoding course of entails inverse quantization and inverse discrete cosine transform (DCT) to recuperate the unique pixel values for every body, and eventually, movement compensation and deblocking to reconstruct and clean out the body.
Decoding could be carried out in software program or {hardware}, with {hardware} decoding being quicker and extra power-efficient, however much less versatile than software program decoding.
Step 3: Post-processing the uncompressed video
This is the optimization of the decoded (intermediate) video knowledge obtained within the earlier step. It entails shade correction, scaling, noise discount, or frame-rate conversion, to adapt the content material to the goal system or software program.
Step 4: Re-encoding the uncompressed video
This is the conversion of the uncompressed + post-processed video frames into a brand new (as soon as once more) compressed video stream, utilizing the codec that was deemed best suited for the goal system or software program again within the Input Stage, earlier than coming into the Transcoding Pipeline.
Several components, together with the selection of codec, the encoding settings, and the complexity of the supply video content material affect the standard of this encoded video stream. By fastidiously deciding on the appropriate codec and encoding settings, the transcoding software program can create a high-quality output video that’s optimized for the goal system or platform.
Step 5: Muxing the encoded video, audio, and subtitle streams into a brand new file
Muxing (multiplexing) is the ultimate step within the video transcoding pipeline. It entails combining the totally different parts of the multimedia file – the processed and re-encoded video, audio, and subtitle streams – right into a single output file.
This course of additionally provides any needed metadata or different info, comparable to a container format or streaming protocol. This may contain including a file header/trailer, checksums, – mainly, every other knowledge that’s required for compatibility with the goal system or software program.
How does transcoding differ from Transrating and Transsizing?
Transcoding, Transrating, and Transsizing are all methods utilized in video processing, however they differ of their targets and the precise facets of the video stream that they modify.
Transcoding is essentially the most common time period, referring to the modification of varied facets of the video stream to create a brand new, optimized output file; whereas Transrating and Transsizing are extra particular methods that target optimizing both the bit fee or the decision, respectively, leaving all the things else unchanged.
Summarizing this as a desk ought to clear issues up.
| Process | Goal | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Transcoding | Convert video from one format/codec to a different to make it suitable with a selected system or platform, whereas additionally decreasing the file measurement as a lot as attainable. | Change format, codec, decision, bitrate, and so forth. |
| Transrating | Reduce the scale of the video stream to accommodate decrease bandwidth connections whereas sustaining the standard of the video. | Change the bitrate of a video stream with out altering the format or decision of the video. |
| Transsizing | Optimize the video for various system/display screen sizes whereas sustaining the standard of the video. | Changing the decision of a video stream with out altering the bitrate or format of the video. |
Types of Video Transcoding
Several types of video transcoding can be utilized. Let’s rapidly evaluate these.
1. Lossless vs. Lossy Transcoding
Lossless transcoding preserves the unique video high quality however may end up in bigger file sizes, whereas Lossy transcoding sacrifices some high quality to realize smaller file sizes, however might not be appropriate for use-cases that prioritize picture high quality.
| Factor | Lossless Transcoding | Lossy Transcoding |
|---|---|---|
| Quality | Maintains authentic high quality, whether or not the conversion was lossless-to-lossless, or lossy-to-lossless. | Discards knowledge that received’t be perceived by most human beings, sacrificing some high quality for a “shut sufficient” end result. |
| File measurement | Typically leads to bigger file sizes. | Typically leads to smaller file sizes. |
| Bitrate | Can keep the identical bitrate or improve it for higher high quality. | Reduces bitrate to cut back file measurement, so inherently sacrifices some high quality. |
| Codecs Typically Used | FFV1, Lagarith, H.264 Lossless, OpenEXR | H.264, H.265, VP9, AV1 |
| Use case | Best for archiving, and preserving authentic high quality. | Best for streaming and supply, the place smaller file sizes are extra necessary than high quality. |
The selection of utilizing lossless transcoding merely is dependent upon whether or not you have to convert to new codecs with out shedding high quality. If the reply isn’t any, lossy transcoding is the best way to go.
2. Interframe Vs. Intraframe transcoding
Inter-frame transcoding analyzes the variations between frames and solely encodes the adjustments, leading to smaller file sizes however increased processing calls for, whereas intra-frame transcoding encodes each body as a standalone picture leading to bigger file sizes however decrease processing calls for.
| Factor | Interframe Transcoding | Intraframe Transcoding |
|---|---|---|
| Compression | Achieves increased compression by referencing neighboring frames, after which compensating for temporal variations. | Achieves much less compression since every body is encoded independently. |
| Quality | A larger danger of high quality degradation, and artifacting. | Maintains high quality, since every body is encoded independently |
| Bitrate | Can obtain the identical high quality at decrease bitrates due to temporal compensation. | Typically wants increased bitrates for a similar high quality, since every body is encoded independently. |
| Decoding | Requires extra processing energy to decode. | Requires much less processing energy to decode. |
| Codecs Typically Used | H.264, MPEG-2, MPEG-4 | Apple ProfessionalRes |
| Use case | Best for streaming and supply, the place smaller file sizes are extra necessary than high quality. | Best for modifying and post-production workflows, the place preservation of high quality is mission-critical. |

The selection between intraframe and interframe transcoding will rely upon the precise use case, the video’s movement, and the specified stability between high quality and file measurement.
3. Format-specific transcoding (e.g., transcoding from H.264 to H.265)
Format-specific transcoding refers back to the strategy of changing a video from one particular mixture of codec and container (H.264 and mp4, for instance) to a different, a well-liked instance being transcoding an H.264 stream to an H.265 stream. It is the classical use case for video transcoding, and relies solely on the necessities of the goal platform or system.
💡
Transcoding from H.264 to H.265 entails decoding the H.264 video stream into uncompressed video frames after which re-encoding these frames into the H.265 format utilizing an H.265 encoder. The course of entails analyzing the unique video stream to find out the best strategy to compress the video utilizing H.265 encoding methods, after which encoding the video with the chosen parameters.
Video transcoding requires highly effective and dependable instruments, and there are a number of applied sciences accessible that may assist. Whether open-source, cloud-based, or prosumer-grade instruments, there’s one for each want and talent stage. Here are a number of widespread selections:
- FFmpeg: FFmpeg is a free and open-source command-line software for video transcoding, encoding, and streaming. It helps a variety of video codecs and codecs and can be utilized on varied platforms, together with Windows, Mac, and Linux.
- Handbrake: Handbrake is a free, open-source video transcoder that’s simple to make use of and accessible for Windows, Mac, and Linux. It helps a variety of video codecs, codecs, and readymade presets for varied units/use-cases, in addition to a number of superior options like batch processing, video filters, and chapter markers.
- Adobe Media Encoder: Adobe Media Encoder is a professional-grade video transcoding software that’s a part of Adobe’s Creative Cloud suite. It helps batch processing and can be utilized to automate complicated transcoding workflows. It additionally consists of presets for particular units and platforms, video filters, and the power so as to add watermarks and captions to movies.
- Open supply transcoding libraries: These widespread open supply transcoding libraries present builders with highly effective instruments for transcoding video content material, in addition to for modifying, processing, and streaming multimedia content material. They are always being up to date and improved, and are broadly utilized by builders world wide.
- x265: x265, equally, is one other free and open-source video encoder library that’s used for encoding HEVC/H.265 video streams as a substitute. Implementing superior H.265 compression methods, it requires much less bitrate than x264 to realize the identical picture high quality.
- AOMedia Video Codec (AV1): AV1 is a free and open-source video codec developed by the Alliance for Open Media (a consortium, together with Google, Amazon, Microsoft, Mozilla, and Netflix, amongst others.) The important purpose of AV1 is to supply a royalty-free various to current video codecs comparable to H.264 and H.265/HEVC, which require licensing charges to be paid to patent holders.
Firefox and Chrome have native assist for AV1, and lots of widespread video transcoding and modifying software program purposes, comparable to HandBrake and OBS Studio, additionally assist AV1 encoding and decoding.
- libvpx: libvpx is a free and open-source video codec library that’s written in C, first launched by Google in 2010 (improved with VP9 in 2013), and designed to supply a free and open various to current video codecs comparable to H.264. VP8/VP9 each present environment friendly compression of video knowledge whereas additionally sustaining excessive visible high quality, making libvpx well-suited to be used in a variety of purposes.
5. Cloud-based transcoding companies: Cloud-based transcoding companies are on-line platforms that present video transcoding capabilities on the cloud, enabling customers to simply transcode, retailer, and handle their video content material. These companies are extremely scalable, cost-effective, versatile, and simple to make use of. Some examples of cloud-based transcoding companies are:
- Amazon Elastic Transcoder: Amazon Elastic Transcoder is a totally managed service that permits customers to transform media recordsdata from their supply format to variations that can play again on units like smartphones, tablets, and PCs.
- Azure Media Services: Azure Media Services is a cloud-based media processing platform that enables customers to encode, bundle, defend, and stream video and audio at scale.
- ImagePackage: ImageKit is a cloud-based picture and video optimization, transformation, and digital asset administration platform that takes care of your total content material pipeline, from optimization to supply.
A key function of ImagePackage is its automated video optimization – which transcodes any uploaded supply video on the fly to an optimal format and optimal bitrate for playback on a consumer’s system, with no work concerned in your half past a easy Dashboard setting.
With ImagePackage, you too can Transrate or Transsize movies (and pictures, too, making it an awesome match for managing your entire static content material!) in real-time, or add Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR) to any saved video with a developer-friendly API, and eventually, leverage Global CDN caches (AWS CloudFront, by default) to ship this video content material to your end-users with diminished latency and improved efficiency.
Best Practices For Video Transcoding
In the video trade, there are some battle-tested, advisable methods and strategies for transcoding video content material. These practices are designed to make sure that video content material suppliers can ship high-quality video to their viewers with improved efficiency and a greater consumer expertise. Here are a few of them:
- Use Two-Pass Variable Bitrate (VBR) Encoding: Variable Bitrate (VBR) encoding is a method that enables the bitrate of a video to differ dynamically based mostly on the complexity of the video content material from second to second, leading to the next high quality video at a smaller file measurement. Two-pass VBR encoding entails analyzing the video within the first go to find out the suitable bitrate after which encoding the video within the second go utilizing the gathered info, for even higher outcomes.[1]
- Know which bitrate to make use of, and when
Choosing the appropriate bitrate and backbone for video encoding is essential to make sure a stability between video high quality and file measurement. Two necessary components when selecting the suitable bitrate and backbone are the kind of content material being encoded, and the audience.High-motion content material requires the next bitrate and backbone to seize the main points, whereas static scenes can use a decrease bitrate and backbone with out affecting the general high quality. The audience’s viewing habits must also be thought of, with social media uploads and dwell streams requiring decrease resolutions and bitrates to make sure clean playback and little-to-no buffering. A bitrate between 1,500 and 4,000 Kbps is appropriate for 720p video, whereas 8,000 and 14,000 Kbps is appropriate for 4K video[1].
- Know your goal units and platforms
When producing video content material, analysis the technical specs and advisable settings for the platforms and units your video might be seen on, making an allowance for components comparable to supported video codecs, display screen measurement, and accessible bandwidth. Are you going to be making VOD content material for YouTube? Here are the recommended settings Google prescribes for it. Are you a Twitch streamer as a substitute? You need to be on top of these guidelines, then.This info could be always altering, so you will need to keep updated. Also, video internet hosting platforms might supply analytics knowledge on video efficiency and playback high quality that may make it easier to optimize content material for particular units and platforms.
- Use {hardware} acceleration for quicker transcoding
Hardware acceleration entails utilizing specialised {hardware} parts comparable to GPUs and DSPs to hurry up video transcoding, which could be computationally intensive.It gives a major increase to encoding velocity and effectivity by offloading sure duties to those {hardware} parts that may carry out sure calculations extra effectively than the CPU, resulting in improved efficiency throughout the board. However, {hardware} compatibility with software program must be thought of earlier than use.
- Use adaptive bitrate streaming: Adaptive bitrate streaming (ABR) adjusts the video high quality in real-time to optimize the viewing expertise based mostly on the consumer’s community situations. This method works by breaking the video into small segments, encoding every phase at a number of high quality ranges, and deciding on the suitable high quality stage for every phase based mostly on the consumer’s community situations.
To use adaptive bitrate streaming, we have to encode our video into a number of variations at totally different bitrates, generate a manifest, an adaptive playlist, and use a video participant that helps this function.
💡
6. Use a cloud transcoding service:
No matter your use-case, a cloud transcoding service like ImageKit will help you streamline your content material pipeline by offloading the resource-intensive job of transcoding (together with automated format conversion), optimizing (dynamic transrating and transsizing), and delivering video, to a totally managed SaaS. Additionally, you get the advantages of requesting Adaptive Bitrate Streaming (ABR)[1] for any of your movies with one line of code, and any rework you possibly can consider, in real-time[2].
This means, you save on investing in costly devoted {hardware} and software program (and sustaining them), by leveraging the infrastructure and processing energy of the cloud supplier to transcode movies at scale, solely paying for what you employ. This provides you quicker turnaround instances in your content material, and larger scalability.
Common use instances for video transcoding
- Compressing massive video recordsdata for simpler storage and sharing
Video transcoding will help compress massive video recordsdata to a smaller measurement with out compromising the video high quality, making it simpler to retailer and share ( rule of thumb is to decrease the bitrate by not more than 20% of the unique bitrate). This is very helpful when coping with high-resolution video recordsdata (or HDR video) that may take up a major quantity of cupboard space. A superb instance of that is video archiving.
By transcoding outdated household movies, historic footage, or different necessary movies that have been recorded in outdated video codecs like VHS (a notoriously fragile bodily media) with codecs like FFV1, we will compress this outdated, uncooked video footage, and convert it to a measurement and format that’s extra appropriate for long-term storage. Here, transcoding ensures that video content material stays accessible and playable at the same time as know-how and codecs evolve over time.
- Optimizing movies for streaming companies (e.g., YouTube, Vimeo)
Transcoding the unique video into a number of variations at totally different bitrates,
resolutions, and codecs ensures that viewers with totally different web speeds and system capabilities can stream the video seamlessly with out buffering or stuttering, leading to a greater viewing expertise.Also, the transcoding course of can add Metadata, (comparable to title, description, and tags) to extend visibility.
- Transcoding movies for modifying or post-production workflows
Transcoding movies for modifying or post-production workflows contain changing uncooked footage from cameras or different sources (that may be large – A 60-minute normal definition video is ~70 GB, whereas a two-hour-long 4k UHD film can be ~3400 GB or 3.4 TB[1]) right into a format that’s extra simply editable, with out dropping frames making an attempt to decode huge movies in actual time, shedding high quality from the supply, or shedding compatibility with the workstation platform.
For instance, the ProRes codec is a well-liked selection for video modifying on Macs, whereas the DNxHD codec is commonly used for Windows-based methods. By transcoding the footage, editors and post-production groups can work extra effectively and successfully, decreasing the period of time and sources wanted to finish initiatives and making certain that the ultimate product is of top of the range.
- Transferring movies over a community
You can use video transcoding on the fly to stream a film (in 4K, encoded utilizing HEVC/H.265, within the MKV format) out of your Media Server, over the web, to your buddy’s Smart TV (on a connection that solely has sufficient bandwidth to assist 1080p movies, with the TV itself solely supporting H.264 movies within the MP4 format) for a gaggle film night time. This is a situation that may not be attainable with out dwell transcoding.
- Adding subtitles or captions to movies utilizing video transcoding
Via transcoding, you might convert the unique video right into a container like MKV that helps native subtitles or captions after which add the subtitles or captions (SRT, VTT, or SSA codecs) to the video.This ensures that viewers can watch the video with subtitles or captions, which is very helpful for accessibility functions or for viewers who converse a unique language.
Conclusion
Video transcoding is a crucial know-how remodeling how we ship and devour video content material. By optimizing video content material for various units and networks, transcoding improves video supply effectivity, enhances the viewer expertise, and allows content material creators and distributors alike to succeed in a wider viewers.
Whether software program or hardware-based, transcoding has additionally been important for enhancing accessibility as video consumption continues to develop. Used proper, it could possibly add subtitles, captions, and different accessibility options, increasing the video’s attain to a wider vary of viewers.
So, it’s truthful to say that the long run outlook for video transcoding is promising, with it taking part in an more and more necessary position in delivering high-quality video content material to a wider viewers whereas additionally enhancing the viewer expertise throughout the board.
Looking for an easy-to-use video transcoding software for scaling your video streaming?
Look no additional than ImagePackage. Sign up for our forever free trial to know what it could possibly do to your video streaming.
https://imagekit.io/weblog/video-transcoding/




